Research Topics/Water Quality Assessment
Targets of Water Quality Assessment
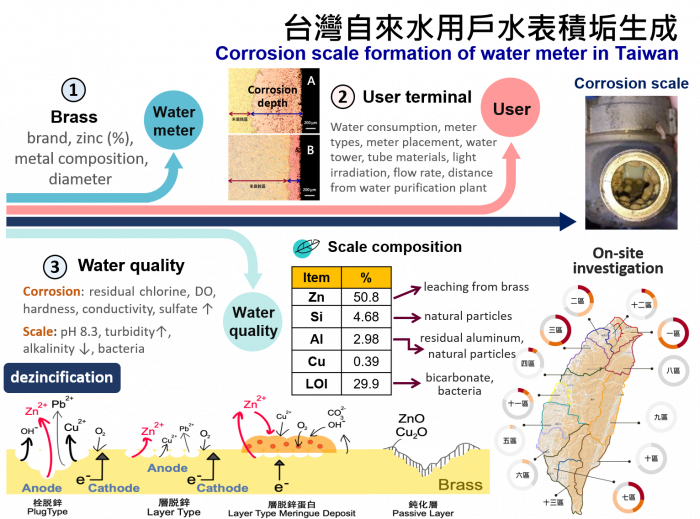
Theme I: Corrosion scale formation of water meter in Taiwan
The dezincification of brass water meters in a water distribution system is affected by tap water characteristics. However, the effects of mixed water quality on corrosion and scale formation on the behaviour of brass water meters have remained unclear. This study investigated the long-term impact of tap water characteristics on the brass dezincification of commercial water meters, using a household-simulated circulating pipeline system. The effect of water anions, alkalinity, and residual chlorine on dezincification and corrosion of such brass water meters were quantitatively and electrochemically examined for over a period of 376 days. The results show that water meters suffer the most severe dezincification when the tap water has a high level of anions and low alkalinity. This study provides a further insight into how tap water characteristics impact the long-term brass dezincification of water meters, which benefits water utilities to forecast scale formation under specific tap water conditions. The findings of this study provided detailed information regarding the main factors that affected brass dezincification under a long-term exposure to mixed parameter water, which would highly benefit water utilities in controlling corrosion and failure of water meters in water distribution systems. This study was published in Environmental Science Water Research & Technology (2021).
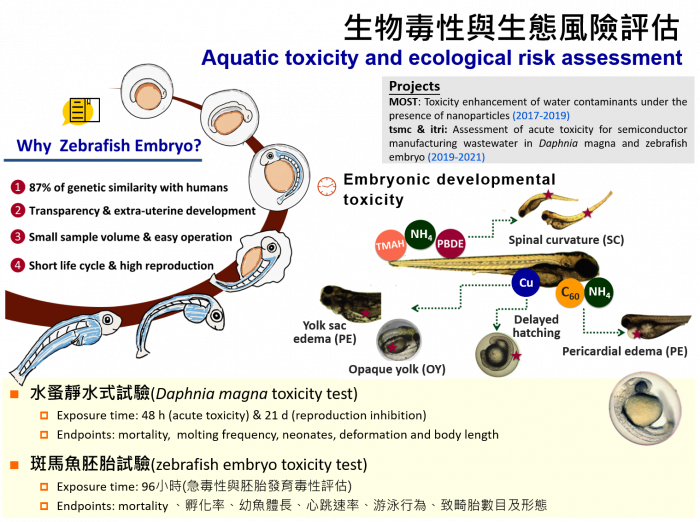
Theme II: Aquatic toxicity and ecological risk assessment
Daphnia magna is a representative species of invertebrate organisms for biological toxicity testing. Our group focused on evaluation of the acute toxicity units (TUa) for semiconductor manufacturing wastewater and discharge, and identification of their toxic contribution. In addition, Daphnia magna can also be applied to evaluate the ecotoxicology effects of emerging pollutants, such as nanoparticles and nanoplastics by observation of deformation, growth inhibition and reproductive inhibition (21-day chronic toxicity test).
Zebrafish (Danio rerio) is a popular model organism used for drug screening and toxicity test in laboratories. However, from the stand of ethical considerations, zebrafish embryo has become an alternate model for eco-toxicity assessments. Furthermore, because of the transparent chorions and rapid extra-uterine development, the phenotypic changes of zebrafish embryo during embryonic development stage is easy to be observed; thus, it has been widely used for assessing pharmacological toxicity, environmental impacts of nanoplastics, nanoparticles, metal ions, pesticides and PBDEs, and industrial effluents. We have published the related research in Chemosphere (2017; 2018) and Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety (2021).
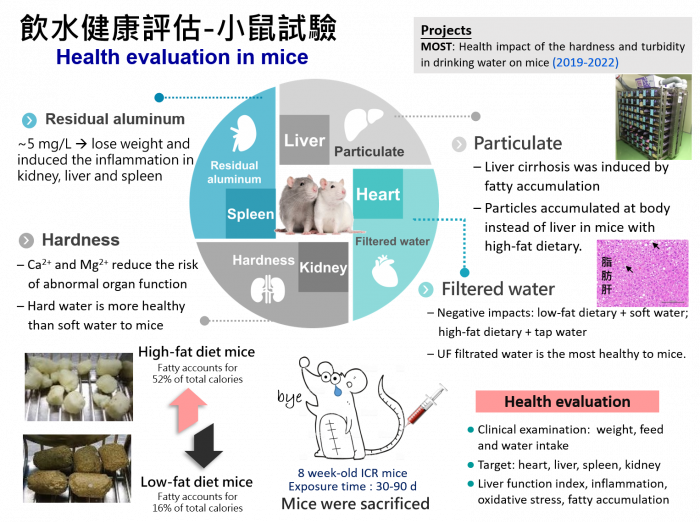
Theme III: Health evaluation in mice
The residual particles and ions in the tap water have been reported to cause damages to human health. Therefore, most water users have installed water filters to ensure the safety of water for drinking purpose. There are various kinds of commercially water filters, such as, ultra-filtration (UF), ion exchange resin (IE), and reverse osmosis (RO) filters. In general, UF filter is frequently applied to effectively remove the particulate matter. On the other hand, IE filter is used to eliminate specific ions; whereas RO filter is used to remove all particles and ions in water. The diversity of filter approach results in the variations in the quality of the filtered water, which might contain trace levels of residual particulates and/or ions. However, the health impacts of such residual particles or ions in drinking water are still unclear. Besides, dietary behavior is other crucial criteria that directly affects human health. High-fat dietary easily results in human obesity and thus increases the risk of getting various diseases. Our finding indicated the abnormal body weight loss of mice could be eliminated when hardness ions existed in the water. Therefore, if particles exist in drinking water, the addition of calcium and magnesium ions could reduce the risk of organ damages for both of HF and LF dietary. At the end of this project, we will recommend a suitable guideline of selection of water filters for people who are under low- and high-fat diets.
